Corporate Strategy: The Fundamental Question
"Why do firms refuse to stay small? If specialization is efficient, why does Amazon sell everything from cloud servers to groceries?"
Business Strategy asks how to compete (Cost vs. Differentiation). Corporate Strategy asks where to compete. Using the Amazon case study, we see a relentless drive to expand boundaries. But growth isn't just about greed; it's a structural necessity driven by five specific engines.
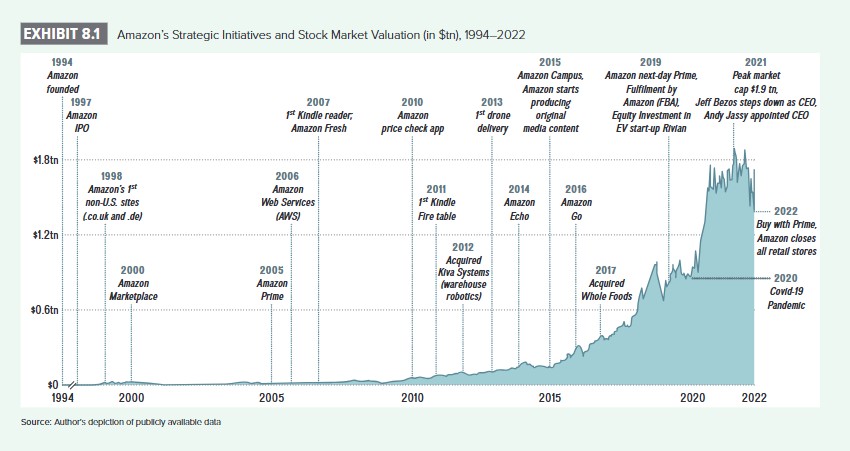
Excerpt: Amazon's evolution from online bookseller to diversified tech giant.
The 5 Drivers of Growth
1. Increase Profitability (Peloton Case) ▼
Profitable growth allows businesses to provide higher returns for shareholders. For publicly traded companies, valuation is determined by expected future profits.
Example: Peloton
The connected fitness company lost over 90% of its market cap, falling from $50 billion to $4 billion. With such a low valuation, it became a prime target for a hostile takeover or leveraged buyout.
2. Lower Costs (Economies of Scale) ▼
3. Increase Market Power ▼
4. Reduce Risk ▼
5. Motivate Management (The Principal-Agent Problem) ▼
Growth offers career opportunities. However, behavioral economics suggests managers may pursue growth for empire building, job security, and perks (corporate jets) rather than profitability.
This is the Principal-Agent Problem: Agents (managers) pursuing goals that conflict with Principals (shareholders).
Three Critical Strategic Questions
Before expanding, every executive must answer these three questions to define the firm's boundaries:
Vertical Integration
In what stages of the industry value chain should the company participate? The industry value chain refers to the transformation of raw materials into finished goods along distinct vertical stages.
Horizontal Diversification
What range of products and services should the company offer?
Geographic Scope
Where should the company compete geographically in terms of regional, national, or international markets?
Visualizing the Strategic Space
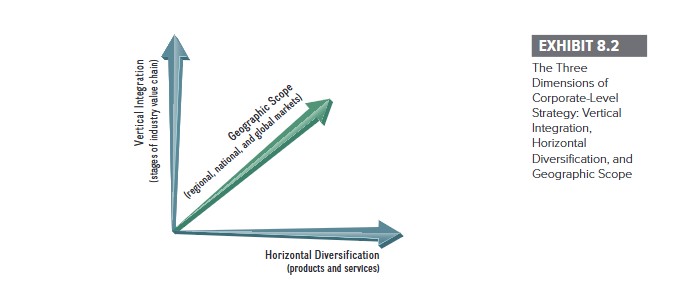
1. Vertical Integration
Owning more of the value chain (e.g., manufacturing inputs or owning retail stores).
2. Horizontal Diversification
Adding new products or services (e.g., selling cloud computing alongside books).
3. Geographic Scope
Expanding into new regions or countries (e.g., entering the Indian market).
Core Strategic Concepts
"What are the underlying economic forces that dictate where a firm should compete?"
The decisions of where to compete are guided by four fundamental concepts:
Core Competencies
Unique strengths embedded deep within a firm. Activities that draw on what the firm knows how to do well (e.g., Amazon's AI algorithms) should be done in-house.
Economies of Scale
Average cost per unit decreases as output increases. Example: AB InBev (Budweiser) captures 50% of global beer profits due to its massive scale.
Economies of Scope
Cost savings from producing two outputs together. Example: Amazon leverages its logistics network to deliver millions of different products efficiently.
Transaction Costs
All costs associated with an economic exchange. This concept answers the "Make or Buy" question.
The Boundaries of the Firm
"Determining boundaries is critical. Given the efficiency of free markets, why do firms exist at all?"
Scholar's Corner: Ronald Coase
Nobel Laureate Ronald Coase initiated this stream of research. The answer to "why firms exist" is Transaction Costs. Markets have friction (search, negotiation, enforcement). When market transaction costs are higher than internal organization costs, firms emerge.
Exhibit 8.3: Internal vs External Costs
📉 Market Transaction Costs
- Search Costs: Finding a vendor.
- Negotiation: Drafting contracts.
- Monitoring: Ensuring compliance.
- Enforcement: Legal costs.
🏢 Internal Transaction Costs
- Administrative Costs: Bureaucracy.
- Low-Powered Incentives: Salaries vs. profits.
- Principal-Agent Loss: Managerial perks.
- Resource Allocation: Internal politics.
The Golden Rule
Vertically Integrate (Make)
Outsource (Buy)
Make: Google's Code
Why does Google hire programmers instead of contracting?
1. Proprietary Assets: Search algorithms are secret.
2. Integration: Tightly coupling Search, Ads, and AI.
Buy: Nike's Manufacturing
Why does Nike outsource production?
1. Commodity Process: Manufacturing shoes is standard.
2. Admin Costs: Owning factories adds huge bureaucracy.
Vertical Integration: Ownership of the Value Chain
"Should you own the cows or just buy the milk? Why did Delta Airlines buy an oil refinery?"
Vertical Integration is about owning the inputs (Backward) or the distribution (Forward). It secures critical supplies and specialized assets but risks reducing flexibility.
Amazon's Integrated Ecosystem
Amazon strategically owns critical parts of its value chain to ensure efficiency and resilience.
Backward Integration (Upstream)
- Logistics Network: Built fleet (Amazon Air) and centers.
- Private-Label: Amazon Basics & Prime Video content.
- Cloud (AWS): Internal IT became a massive service product.
Forward Integration (Downstream)
- Direct-to-Consumer: Eliminating middlemen.
- Physical Retail: Whole Foods, Amazon Go.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Branded vans & Flex drivers.
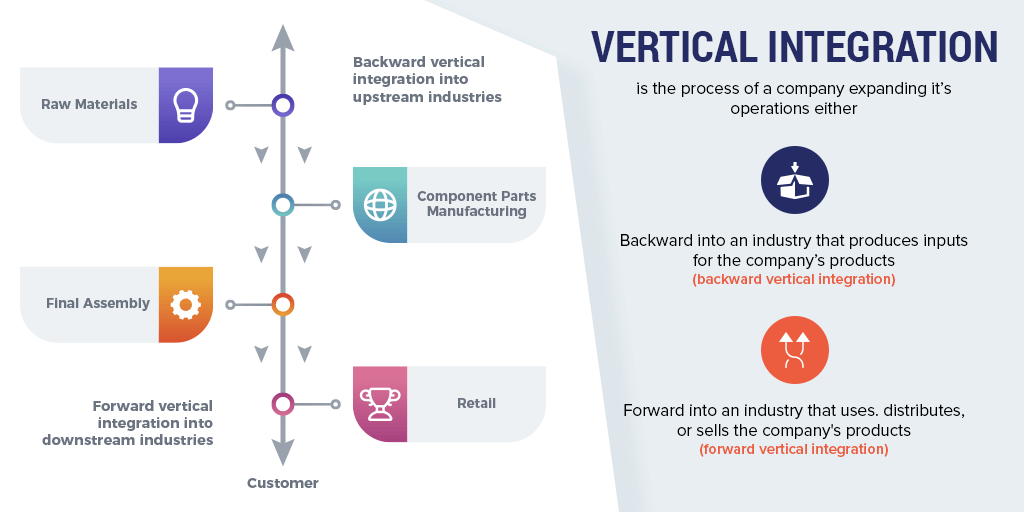
Stage 1: Raw Materials
Stage 2: Components
Stage 3: Assembly
Stage 4: Sales
Strategic Case: HTC vs. Apple
HTC integrated Backward into design and Forward into sales to capture value.
Apple captures 95% of profits by focusing on Stage 1 & 4 (Smiley Curve).
Diversification: The Empire Building Logic
"Is it genius or madness for a company to sell motorcycles, pianos, and financial services? (Yamaha)"
1. Single Business
>95% RevenueEx: Coca-Cola
2. Dominant Business
70-95% RevenueEx: Harley-Davidson
3. Related Diversification
<70% RevenueEx: Amazon, Nike
4. Unrelated (Conglomerate)
<70% RevenueEx: Berkshire Hathaway
The Diversification-Performance Inverted U
Core Competence-Market Matrix
"We have a great engine. Should we build a better car (Leverage) or build a jet (Redeploy)?"
Redeploying
Mega-Opportunities
Leveraging
Building
Strategy Simulator
"Can you run a multi-billion dollar empire without destroying shareholder value?"
Choose Your Role
Scenario
Simulation Complete
Knowledge Check
"Test your understanding of Corporate Strategy concepts."